NFC for remote onboarding
What is AML?
Create secure compliance with anti-money laundering regulations no matter your industry.

Anti-Money Laundering
Compliance and Security for AML legislation
We explain AML and how ReadID can help:
- What is AML?
- What is the difference between AML, CDD, and KYC?
- Why is AML important?
- A brief history of AML
- How is AML applied in practice?
- How can ReadID improve your AML compliance?
What is AML?
AML stands for Anti-Money Laundering and refers to the laws and regulations that exist to prevent criminals from disguising illegally obtained funds as legitimate income- this is the act of ‘money laundering’, washing funds of their illicit origins to evade detection. Many terms fall under the umbrella of AML, including Customer Due Diligence (CDD) and Know Your Customer (KYC). For an in-depth explanation of KYC and how remote identity verification can help streamline your KYC processes, view our What is KYC? page.
What is the difference between AML, CDD, and KYC?
AML is the broad set of regulations and laws in place that aim to deter money laundering. KYC and CDD are processes and tools that carry out AML legislation to ensure concerned parties are complying with these AML regulations. Customer Due Diligence describes the scrutiny financial institutions are required to apply under AML legislation to identify and report suspicious activity of their customers. Know Your Customer on the other hand are processes that apply Customer Due Diligence in a practical manner, including verifying potential clients and customers’ identities.
Why is AML important?
Anti-money laundering legislation is a vital component to protect customers and financial institutions in today’s increasingly digital world. By complying with AML legislation, banks protect themselves and therefore their customers from financial penalties, such as fines. Furthermore, these processes catch fraudsters early in the process of potential money laundering and stop them in their tracks, preventing illegitimate funds from entering circulation.
As more forms of digital, and therefore harder to regulate, currencies grow in their use and acceptance, it is important that AML legislation and processes keep pace in sophistication, ease of implementation, and ease of use for end customers. They must also provide a high level of security and assurance for financial institutions, making NFC First an ideal approach to AML.

A brief history of AML
Anti-money laundering initiatives increased globally following the creation of the Financial Action Task Force in 1989. This group was established to develop international standards and tackle money laundering and promote the implementation of these standards in different countries around the world. In Europe, these kinds of regulations are implemented through the Anti-Money Laundering Directive (AMLD). This directive has developed over many iterations, most recently with the sixth AMLD in June of 2021.
NFC has better conversion, much better
Who needs to comply with AML?
Financial institutions such as banks, brokers, and other businesses are legally required to follow AML directives on both a national and international level, and this compliance is often achieved by robust KYC processes. With methods of digital transactions rapidly changing and growing, it is more important than ever that new forms of technology, like cryptocurrency, are regulated within AML legislation. Inverid prides ourselves on our ability to innovate and provide the best in NFC technology. We host an extensive list of customers in the financial service industry across the globe, including ING, ASB, ABN AMRO Moneyou, Florius, Aegon, Rabobank, de Volksbank, and more.
How is AML applied in practice?
As previously mentioned, AML is applied practically through CDD and KYC processes. A robust set of processes should include:
- Transaction screening mechanisms (CDD)
- Verifying the identity of potential customers and reverifying them periodically (KYC)
An example of these processes in practice is customer onboarding for ING in The Netherlands, where new customers are required to verify their identity when opening an account. This is achieved via the use of ReadID technology, which ING implemented into their own app. By using an electronic identity document such as a passport, identity card, or residence permit, ING customers can use their smartphone’s NFC capability to easily verify their identity and start mobile banking.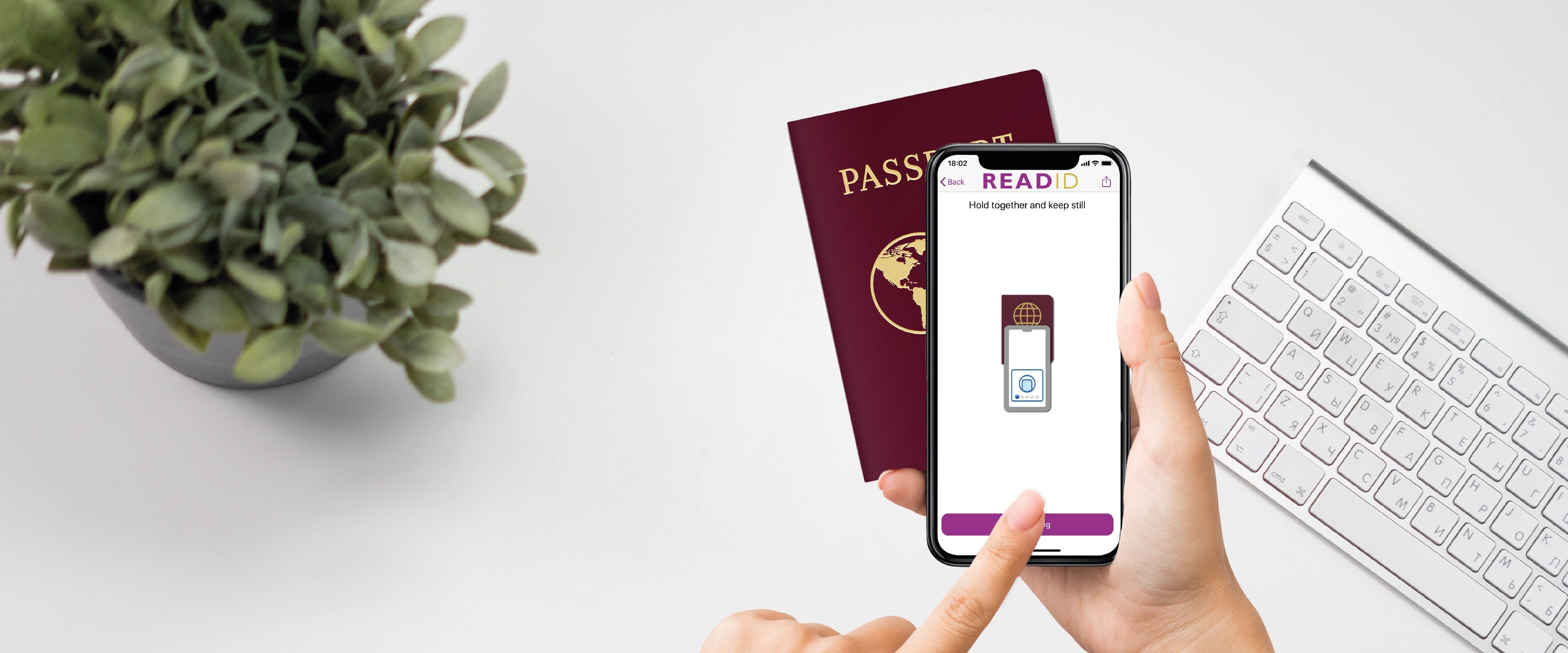
How can ReadID improve your AML compliance?
A cornerstone of AML compliance is having a secure set of Know Your Customer and Customer Due Diligence practices. But how do you as a financial institution maintain the highest level of security assurance while maintaining an enjoyable and speedy process for the end customer? The answer is simple; remote identity verification via a mobile application and NFC, made possible by ReadID. NFC by its very nature is highly secure, with document chips featuring many inherent security features, such as country signing certificates from issuing authorities for document authenticity checks, and NFC producing no reading errors that can be present in OCR verification methods.
All verification is done on ReadID’s secure cloud server, ensuring full compliance with privacy laws and directives such as GDPR, and keeping your customer’s data safe. There is also exceptional document and device coverage. ReadID is proven to work on over 2600 models of devices and as of 2022, 170+ countries produce electronic identity documents. Finally, ReadID not only provides compliance but also conversion- Rabobank saw their conversion almost double after implementing ReadID into their app.

Let’s talk about your AML challenge.
Are you interested in adopting ReadID IDV within your own AML solution? Let’s talk, and see how our software fits within your bigger picture.
Converting, scalable, easy-to-use, and secure NFC-based identity verification.
Subscribe for our Inverid Newsletter
ISO/IEC 27001 certified

ISO/IEC 27701 certified

eIDAS module certifications

SOC2 type 2

Cyber Essentials Plus
